The Chevy Silverado lineup includes three primary classes: the 1500 (light-duty), 2500 (heavy-duty), and 3500 (extreme-duty) models. Each model is engineered for different performance expectations, job requirements, and modification paths. Whether your priority is daily driving comfort or maximum towing force, understanding the distinctions helps in choosing the right model and upgrades.
Overview of the Chevy Silverado Lineup
The Silverado nameplate has served as a core part of Chevrolet’s truck identity since 1998. The series has grown into a leading choice in work, commercial, and personal-use trucks due to its durability and power. While all Silverado models share a similar design language, their performance expectations vary significantly.
The Silverado lineup scales upward in frame strength, towing capacity, and engine output from 1500 → 2500 → 3500. This structure allows drivers to choose based on work demand rather than size alone.
Silverado 1500: Light-Duty Versatility
The Silverado 1500 is designed for a mix of comfort and capability. It offers multiple gasoline and diesel engines and is commonly used for commuting, hauling equipment, and weekend towing.
It supports strong aftermarket modification potential, especially in performance exhaust and intake improvements. This makes it popular among enthusiasts who want personalization along with everyday practicality.

Silverado 2500: Heavy-Duty Strength
The Silverado 2500 HD is built with a reinforced frame and upgraded suspension components to support heavier loads. It is often used in construction, commercial hauling, agricultural work, and off-road field operations.
The engine lineup focuses on torque delivery, allowing the truck to tow significantly more weight than the 1500. Ride comfort remains reasonable, but the 2500 prioritizes work performance above daily softness.

Silverado 3500: Maximum Towing and Payload Capability
The Silverado 3500 HD is the highest-capacity model in the lineup. It features the most robust frame, axle, and suspension design for maximum towing and payload capability. This model is commonly used for equipment trailers, livestock hauling, and commercial tow applications.
Dual-rear-wheel (DRW) configurations are available to improve stability under extreme loads. This model is built primarily for work environments rather than everyday driving comfort.

Engine Options Across the Silverado Lineup
The Silverado offers a range of engines optimized for power, efficiency, or high-torque output depending on model class. Below is a comparison of commonly available engines:
| Engine | Horsepower | Torque (lb-ft) | Model Availability | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.3L V6 | 285 hp | 305 lb-ft | 1500 | Daily driving, general light-duty hauling |
| 5.3L V8 | 355 hp | 383 lb-ft | 1500 / 2500 (select years) | Balanced towing and fuel efficiency |
| 6.2L V8 | 420 hp | 460 lb-ft | 1500 | Maximum gas-engine performance |
| 6.6L V8 Gas | 401 hp | 464 lb-ft | 2500 / 3500 | Heavy-duty hauling without diesel |
| 6.6L Turbo Diesel V8 | 470 hp | 975 lb-ft | 2500 / 3500 | Maximum towing and torque-driven applications |
| 3.0L Turbo Diesel Inline-6 | 277 hp | 460 lb-ft | 1500 | Long-distance towing and highway efficiency |
Source: GM Official Powertrain Specifications, SAE J1349 certified ratings.
Towing and Payload Capability: Comparing 1500, 2500, and 3500
| Model | Max Towing Capacity | Max Payload | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silverado 1500 | Up to ~13,300 lbs | ~2,300 lbs | Everyday driving with occasional heavy hauling |
| Silverado 2500 | Up to ~22,500 lbs | ~3,900 lbs | Regular heavy-duty hauling and worksite use |
| Silverado 3500 | Up to ~36,000 lbs (DRW) | ~7,400 lbs | Maximum commercial and industrial load handling |
Data referenced from SAE Towing Capabilities Guide and GM Fleet Specifications.
Exhaust Modifications Across the Silverado Lineup
Performance exhaust upgrades improve airflow, reduce exhaust restriction, and enhance engine response.
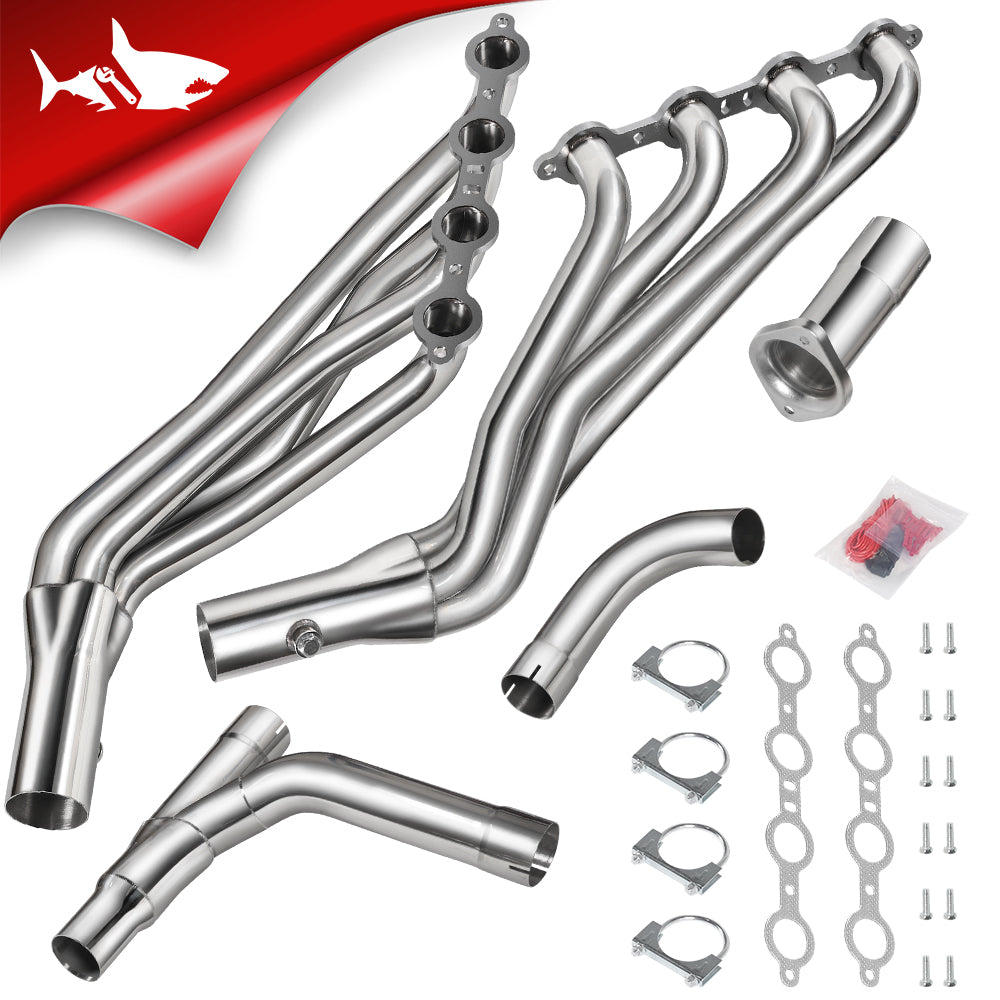
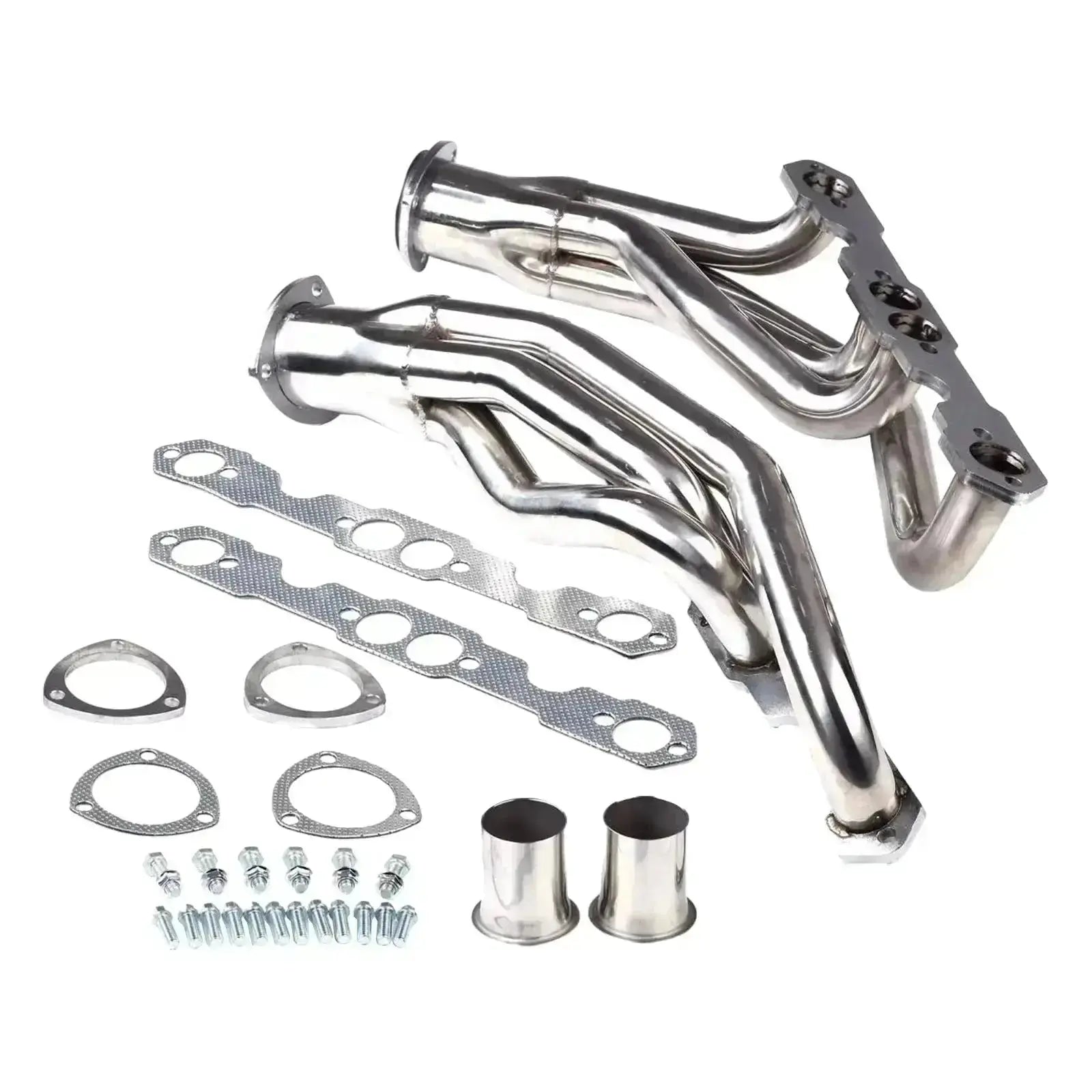
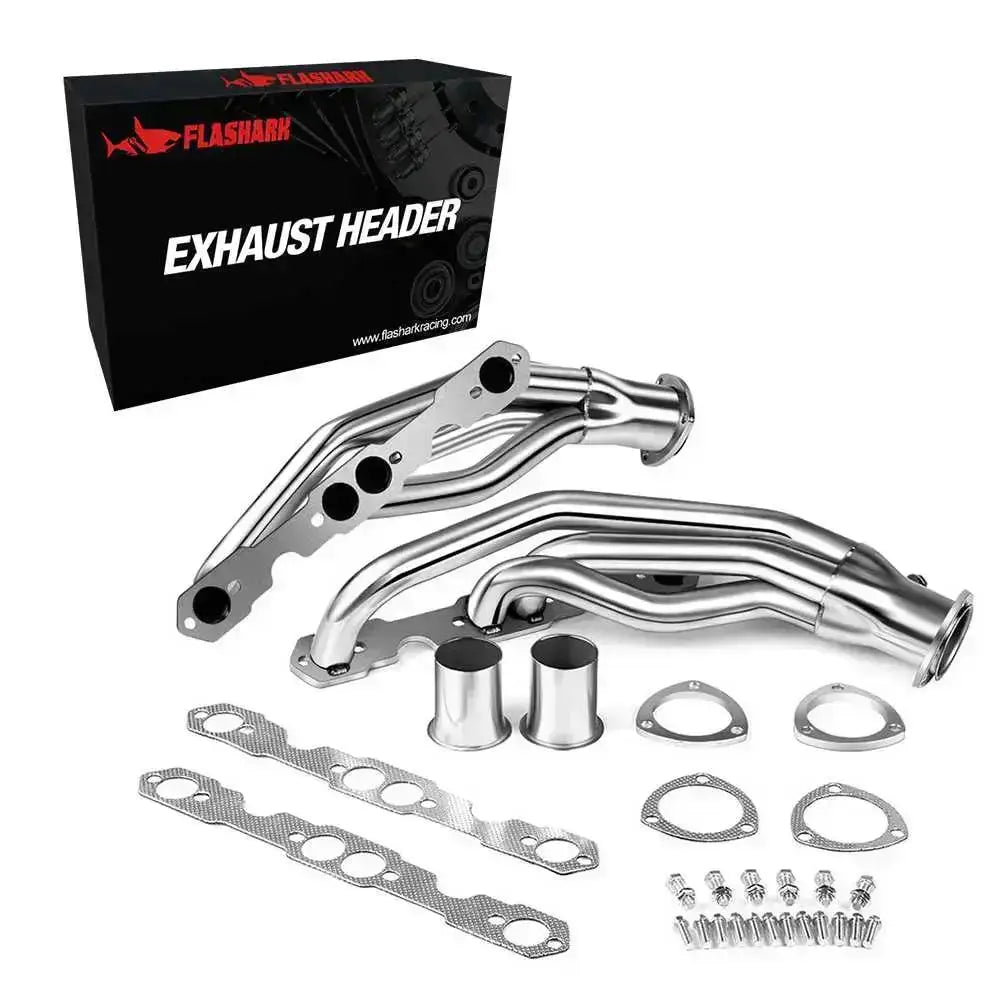
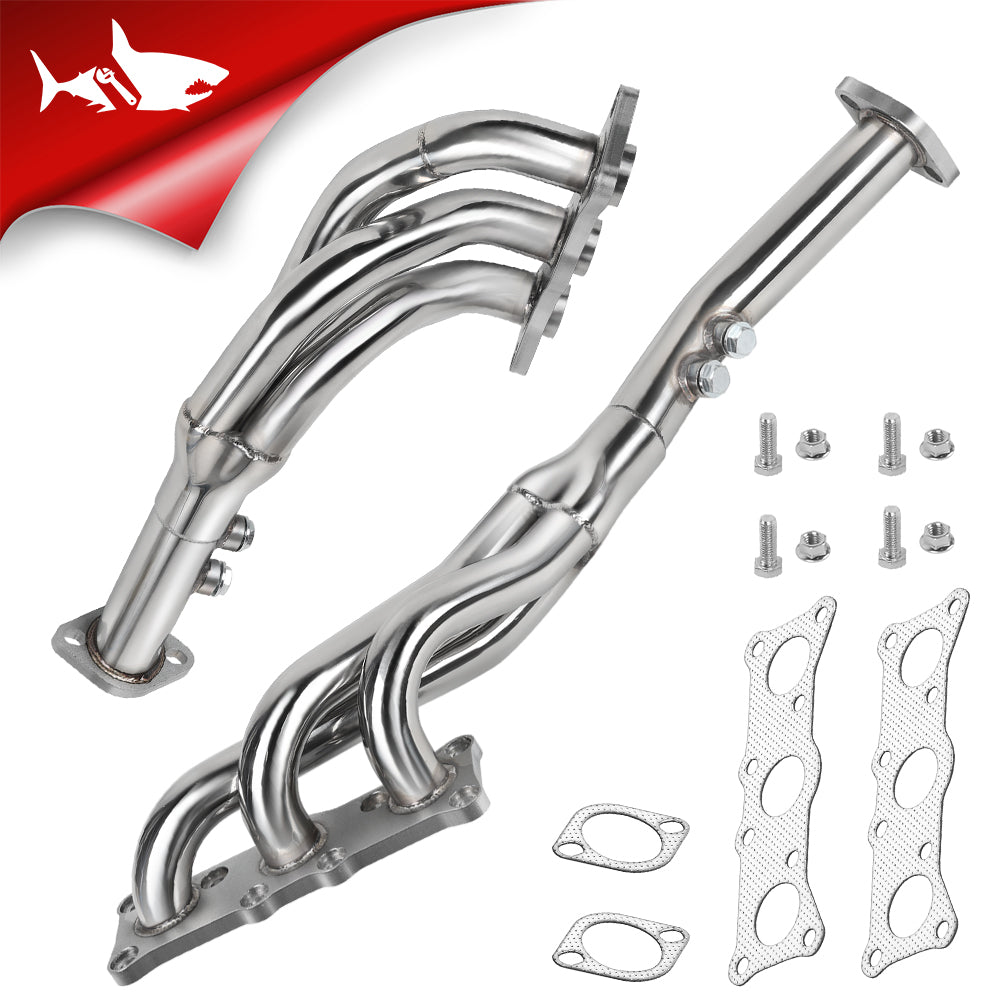
Headers
Upgraded Silverado headers optimize exhaust flow directly from the cylinder heads. This reduces backpressure and improves torque. The benefit is felt most on 1500 gas engines, particularly V8 configurations.

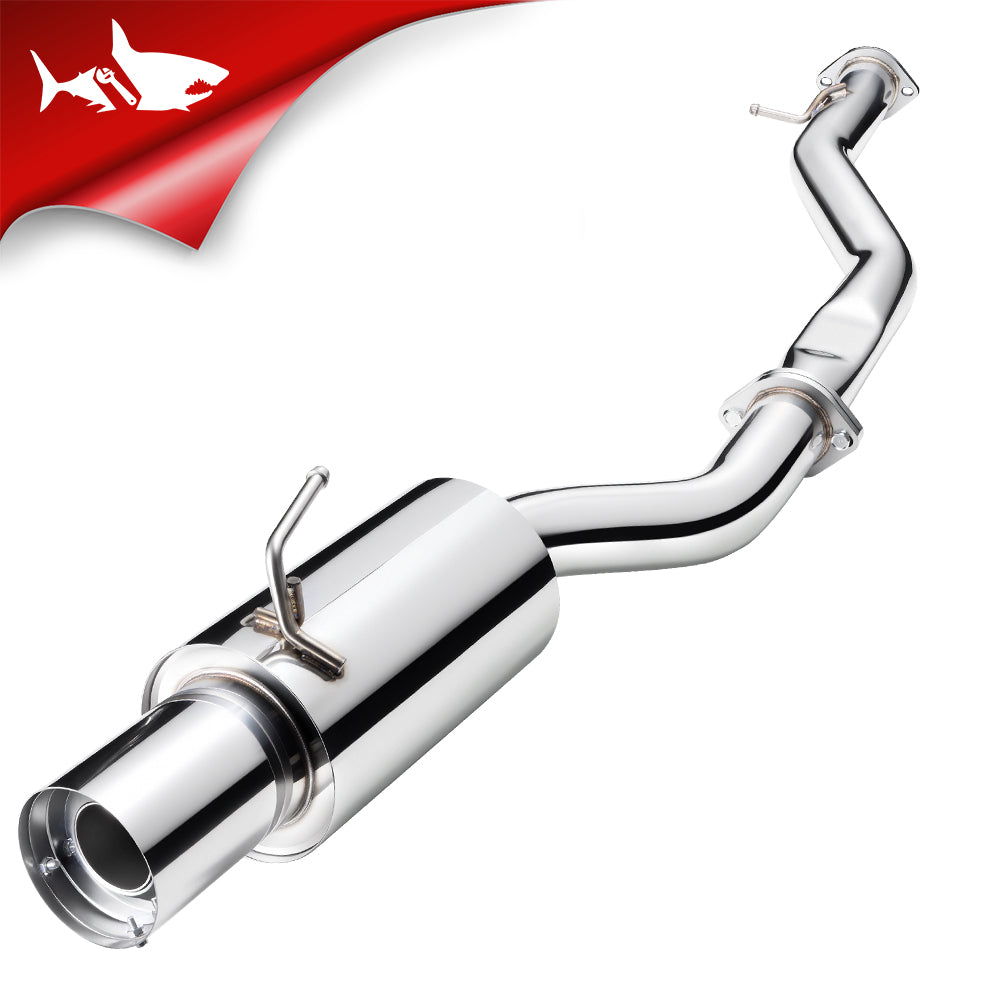
Catback Exhaust Systems
A catback system enhances exhaust note and flow characteristics from the catalytic converter back. This upgrade benefits all three Silverado models by improving high-RPM efficiency and engine tone without altering emissions equipment.
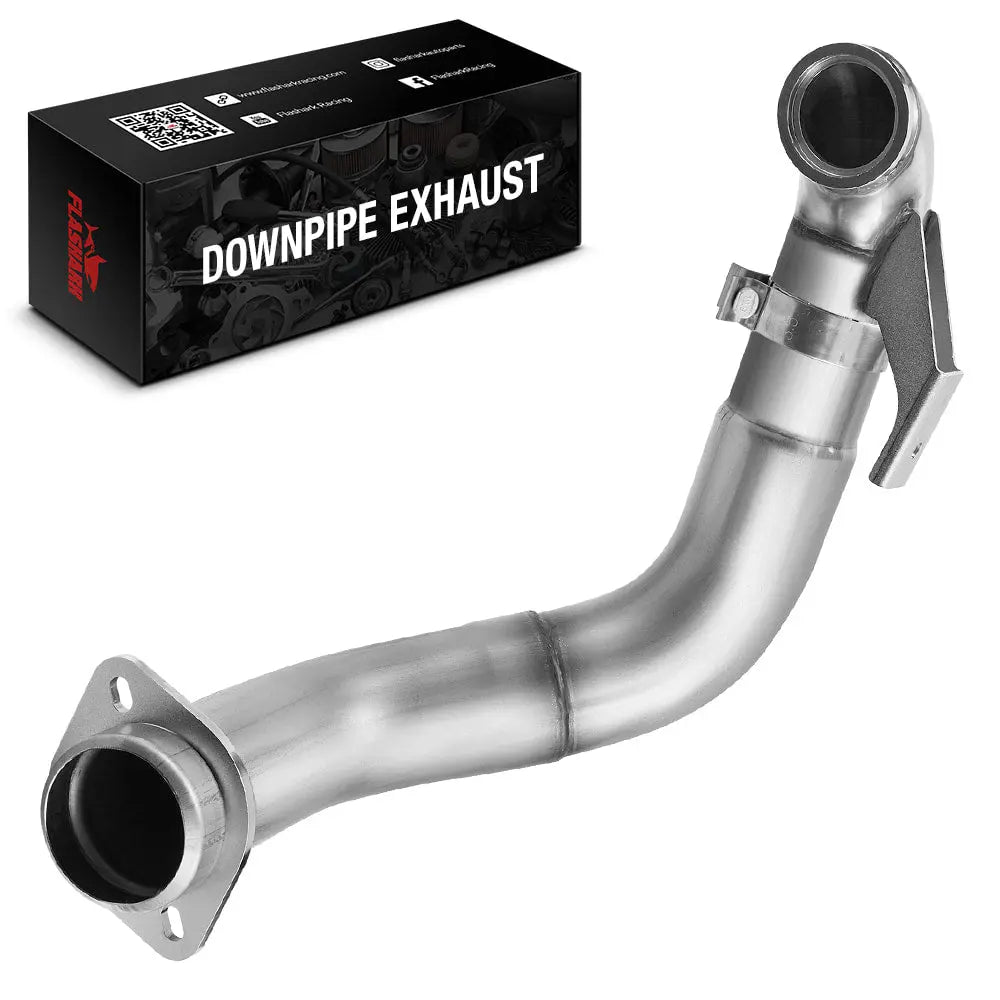
Downpipes
On turbocharged diesel Silverado engines, a performance Silverado downpipe reduces temperature and restriction near the turbine housing. This improves turbo spool time and acceleration response.

Intake Modifications Across Silverado Models
Improving intake airflow increases combustion efficiency and throttle sensitivity.
Cold Air Intake Systems
Cold air intakes draw cooler air from outside the engine compartment. Cooler air holds more oxygen, increasing combustion energy. This upgrade is popular on both gas and diesel engines.
Performance Intake Manifolds
For drivers seeking higher horsepower gains, a performance intake manifold provides smoother, higher-volume airflow to the cylinders. This is most impactful when combined with exhaust and ECU recalibration.
ECU Optimization and Performance Calibration
ECU tuning synchronizes fuel mapping, ignition timing, boost pressure (diesel), and throttle control with new airflow characteristics. Proper calibration ensures smooth drivability and prevents diagnostic errors following modifications.
Conclusion
The Chevy Silverado lineup offers a powertrain and chassis structure appropriate for nearly any use case. The 1500 is best suited for versatile daily performance, the 2500 targets consistent heavy-duty workloads, and the 3500 excels in maximum strain towing environments.
Performance upgrades such as headers, catback exhaust systems, downpipes, cold air intakes, and ECU tuning allow Silverado owners across all models to unlock improved power, responsiveness, and driving engagement. Selecting the right Silverado model and modification path depends entirely on intended use and performance priorities.