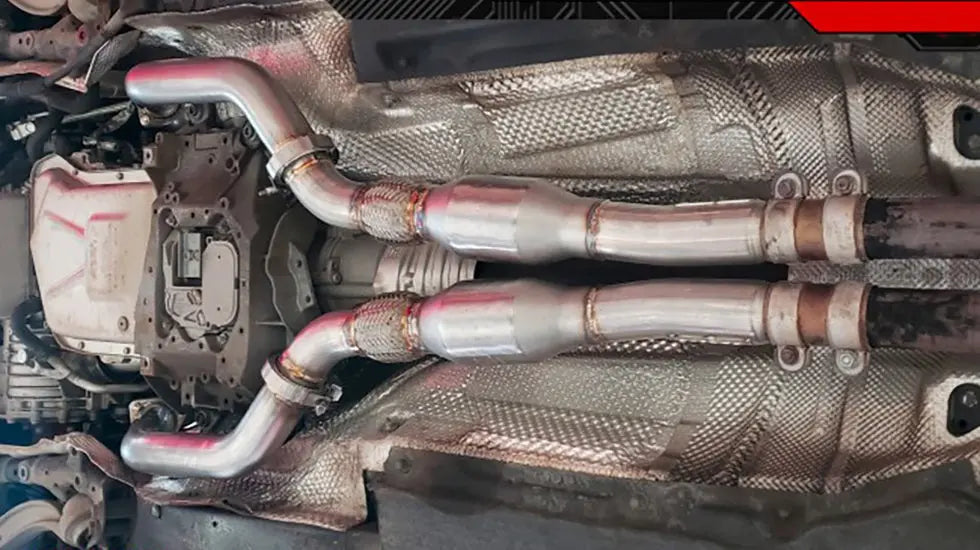
A catted downpipe is a key component in a vehicle's exhaust system that helps manage engine emissions while potentially improving overall performance. Unlike a catless downpipe, which lacks a catalytic converter, a catted downpipe retains this important element. Understanding the role of a catted downpipe, its benefits, and its potential drawbacks is essential for vehicle enthusiasts and anyone looking to enhance their car's exhaust system.
Understanding Downpipes in Automotive Systems
Before diving into the specifics of catted downpipes, it's important to understand what a downpipe is and how it contributes to your vehicle's performance.
What is a Downpipe?
A downpipe is an integral part of the exhaust system in vehicles with turbocharged engines. It connects the turbocharger's exhaust outlet to the rest of the exhaust system, directing the gases out of the engine. The main function of the downpipe is to improve exhaust flow and reduce turbo lag, allowing for quicker spool-up times and more responsive power delivery.
By facilitating better airflow, a downpipe can also contribute to a noticeable improvement in engine performance, such as increased horsepower and torque. The improved exhaust flow helps the turbocharger to operate more efficiently, thus reducing restrictions in the engine's air intake system.
How Downpipes Affect Vehicle Performance
The performance benefits of a downpipe are particularly evident in turbocharged engines. By reducing exhaust backpressure, a downpipe allows gases to exit the turbocharger more freely, leading to faster turbo spool times. This can result in a significant increase in power output, particularly at higher RPMs.
While a downpipe alone won’t dramatically change the engine’s characteristics, it acts as a crucial piece of the puzzle in a complete performance exhaust system, working in conjunction with other modifications like an upgraded intercooler or performance air intake.
What Makes a Downpipe "Catted"?
To understand the significance of a catted downpipe, it's crucial to recognize what distinguishes it from a catless downpipe.
The Role of the Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is a device in the exhaust system that reduces harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances. The catalytic converter works by facilitating chemical reactions that break down pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons, which are then expelled as safer gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor.

In a catted downpipe, this crucial component is retained, ensuring that the vehicle complies with environmental regulations. The catalytic converter reduces the overall environmental impact of the vehicle's emissions, making it an essential feature for those seeking to minimize their carbon footprint.
How Catted Downpipes Differ from Catless Downpipes
The key difference between a catted and catless downpipe lies in the presence of the catalytic converter. Catless downpipes are designed without a catalytic converter, allowing exhaust gases to flow more freely and providing a performance boost. However, this comes at the cost of increased emissions, which can make the vehicle illegal in some regions due to strict emissions laws.
On the other hand, catted downpipes retain the catalytic converter, offering a balance between performance gains and environmental responsibility. While they may not offer as much of a performance boost as catless downpipes, catted downpipes still provide improved airflow over stock systems, which can result in increased horsepower and quicker turbo spool times.
Benefits of Installing a Catted Downpipe
Installing a catted downpipe offers several advantages, especially for those looking for a combination of performance and emissions control.

Emission Control and Environmental Considerations
The most significant advantage of a catted downpipe is its ability to reduce harmful emissions. By retaining the catalytic converter, a catted downpipe helps the vehicle meet emission standards and regulations. This is particularly important for drivers who live in regions with strict emissions laws, such as California or parts of Europe.
Without a catalytic converter, a catless downpipe would significantly increase the vehicle’s output of pollutants, potentially violating local laws and resulting in fines or failed emissions tests. A catted downpipe ensures the vehicle runs cleaner, reducing its environmental impact while still offering performance benefits.
Legal Compliance and Vehicle Inspections
In many states and countries, vehicles must pass emissions tests to be legally driven on public roads. Installing a catted downpipe ensures that your car remains compliant with these laws. A catless downpipe, while offering greater performance, can often result in the vehicle failing emissions inspections, especially in places with strict regulations.
By choosing a catted downpipe, you’re also ensuring that your vehicle will pass inspections without any issues, making it a practical option for everyday drivers who still want a performance upgrade.
Balanced Performance Gains
Catted downpipes offer a significant improvement in performance over stock systems, although not as much as catless versions. They reduce exhaust backpressure, which improves turbo efficiency and can lead to better throttle response and more horsepower. While the power gains are less than a catless downpipe, the improvement is still noticeable, especially when paired with other performance upgrades.
Potential Downsides of Catted Downpipes
While there are many benefits to installing a catted downpipe, it’s important to consider potential downsides.
Power Gains vs. Restrictions
Although catted downpipes offer performance improvements over stock systems, the inclusion of the catalytic converter can create some restrictions in exhaust flow. This means that the performance gains won’t be as pronounced as they would be with a catless downpipe.
For those seeking maximum horsepower and minimal restrictions, a catless downpipe would be a better choice. However, for those who prioritize compliance with emissions standards, a catted downpipe is the preferred option despite the slight compromise in power.
Installation Complexity
Installing a catted downpipe can be a more involved process compared to standard exhaust upgrades. It may require specific modifications to the exhaust system, and depending on the vehicle, it could involve removing or relocating certain components. Additionally, professional installation may be necessary, which can add to the overall cost.
While a catted downpipe is generally easier to install than a catless one, it’s important to understand the requirements for your specific vehicle before starting the installation process.
Choosing Between a Catted and Catless Downpipe
The decision between a catted and a catless downpipe ultimately depends on your priorities—whether it’s performance, emissions control, or legal compliance.
Performance Goals
If maximizing performance is your goal, a catless downpipe may be the right choice. Without the catalytic converter, exhaust gases can flow more freely, allowing for faster turbo spool times and more power at high RPMs. However, this comes with the trade-off of higher emissions and potential legal issues.
If you are looking for a compromise between performance and environmental responsibility, a catted downpipe will offer performance gains while still maintaining cleaner emissions.
Legal and Emission Considerations
If your vehicle must pass emissions inspections or if you live in an area with strict environmental laws, a catted downpipe is the better option. It provides a balance between performance and legal compliance, ensuring that your vehicle adheres to regulations without compromising on too much power.
Noise and Comfort
One of the reasons some drivers opt for a catted downpipe over a catless version is to minimize exhaust noise. While catless downpipes often produce a much louder exhaust note, catted downpipes tend to keep the noise at a more acceptable level, especially for daily driving.
Installation and Maintenance of a Catted Downpipe
Installing and maintaining a catted downpipe is crucial for ensuring its longevity and effectiveness.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Installing a catted downpipe typically involves removing the stock downpipe, fitting the new catted version, and ensuring that the catalytic converter is properly positioned in the exhaust system. This process may require specific tools, including a jack to lift the vehicle, a socket set, and potentially a pipe cutter or exhaust clamp.
It’s always recommended to have the installation done by a professional mechanic, especially if your vehicle has complex exhaust components. Incorrect installation can lead to exhaust leaks, decreased performance, or even engine damage.
Long-Term Maintenance
Catted downpipes are relatively low-maintenance components. However, over time, the catalytic converter can become clogged or worn out, reducing its effectiveness. Regular maintenance of the exhaust system, such as cleaning and checking for blockages, can help ensure that the downpipe functions efficiently for the long term.
Is a Catted Downpipe Right for Your Vehicle?
Choosing a catted downpipe is a practical option for those who want to improve their vehicle’s performance while maintaining legal compliance and minimizing environmental impact. It offers a balanced solution for enthusiasts who aren’t willing to sacrifice emissions control for power.
When to Choose a Catted Downpipe
If you want to enjoy enhanced performance, pass emissions tests, and keep your car street legal, a catted downpipe is the right choice. For those who prefer a balance of power and responsibility, this is an ideal upgrade.
Alternative Solutions
If performance is your sole focus, you might consider a catless downpipe or exploring other performance parts like high-flow catalytic converters or turbo upgrades. These alternatives can offer even greater performance gains but may come at the cost of increased emissions and potential legal challenges.
Conclusion
To wrap it up, a catted downpipe strikes a balance between performance improvement and emissions control. While it may not provide the extreme power gains of a catless version, it offers better exhaust flow and complies with environmental standards, making it a practical choice for most drivers. Ultimately, if you’re looking for an upgrade that boosts turbo performance while staying legal, a catted downpipe is an ideal option for your vehicle.