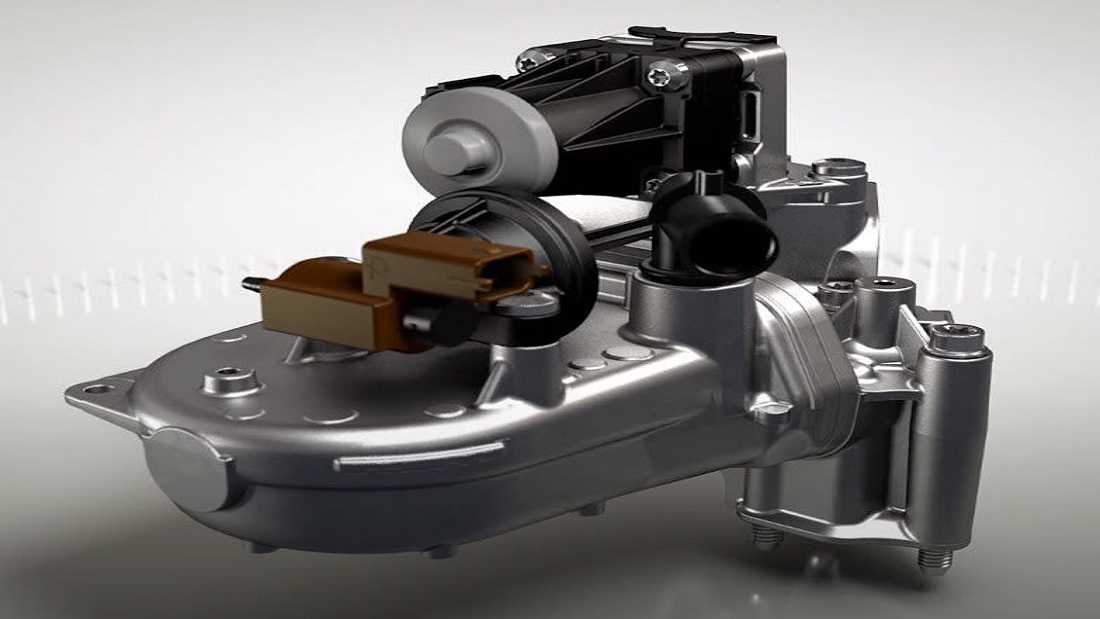
One technique to lessen the engine's hazardous emissions is the exhaust gas recirculation system. It is a crucial component of your engine system, and, like all heavy-duty parts, it must function in a very demanding environment.
But why is it necessary to cool the exhaust gases passing through this system? How can you tell if your engine's cooler is failing? Why does it require cleaning? Can you stop the failure of your EGR cooler? To guarantee the longevity of your EGR cooler and safeguard your engine, keep reading for the answers to these and other concerns.What does an EGR cooler do?
More types of pollutants exist than merely the unburned engine exhaust gases. They can also develop when the combustion chamber of your diesel engine's intense heat breaks chemical bonds, creating new molecules. This heat causes airborne nitrogen and oxygen atoms to mix, forming nitrous oxides (NOx) and ozone (O3). Acid rain can result from NOx combined with water to create smog. Although the ozone layer helps shield humans from UV rays, breathing this gas at ground level can be difficult, especially for people with sensitive lungs or other respiratory ailments.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) decreases combustion temperatures by adding a tiny amount of inert exhaust gas to the air/fuel mixture. Your engine's performance is maintained at a high level while the likelihood of pollutant deposits is greatly reduced. When the exhaust gas is cool, the air/gas mixture is diluted most effectively, which is why the EGR cooler was created.
The EGR cooler, which is located between the turbo and the EGR valve, is a water-to-air heat exchanger. The hot exhaust gas passes through a hollow tube or set of tubes in the body. There are multiple coolant routes all around these tubes. The walls separating the coolant from the exhaust transmit heat, giving cooler, inert exhaust gases prepared to lower the peak combustion temperatures. The vehicle's computer uses the EGR valve to regulate the flow of exhaust gases via the EGR cooler.
The cooling system of the car receives heat from the exhaust system. Simply put, the radiator dissipates the extra heat. However, because the EGR cooler connects your engine's cooling and exhaust systems, problems with the cooler could also result in coolant loss, overheating, and engine damage.
EGR Delete or EGR Cooler Delete?
Let's dispel some myths about the EGR delete kit.
You may come across something called EGR Delete if your EGR cooler is defective or if you simply want to avoid an EGR cooler failure.
Before you go with your purchase, let's take a moment to make sure you have all the knowledge you need to make the greatest choice for getting a truck that will be genuinely reliable.
There is also another crucial aspect to consider in addition to the legality of an EGR delete.
It's possible that your EGR cooler isn't receiving enough coolant if it's failing.
This may indicate that your OEM oil cooler or failing water pump is malfunctioning. In other words, your EGR Cooler is attempting to communicate with you. You run the risk of creating far more serious issues that will cost a lot more money if you delete your EGR cooler without first figuring out why it failed.
Years of experience dealing with the pattern failure in the 6L engine have led us to the conclusion that the engine cooler is frequently the problem's primary cause. Check this to better understand the issue with the oil cooler that came with the original equipment: The engine oil cooler from the factory has a problem.
A rupture or clogged EGR cooler might happen on other engines even though the EGR cooler has enough coolant, even though blocked coolant flow is a common reason for a 6.0 EGR cooler failure.
Most OE EGR coolers use a shell and tube heat exchanger version that uses flat tubes with internal channels. Due to thermal expansion, these flat tubes are prone to fracture, and/or tiny channels can become blocked with soot.
How Important are EGR Coolers?
The EGR reduces NOx emissions by recirculating exhaust gas. This is essential because NOx emissions contribute to smog and acid rain and are extremely harmful! They also contribute to crowded regions having poor air quality, which is detrimental to those who have respiratory conditions like asthma. The cooler is an essential component of the EGR because it lowers the combustion temperature by adding cooled exhaust gas to the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder. As a result, the engine is prevented from overheating, and hot parts like the cylinder head work better due to the lower temperatures.
What Happens When the EGR Cooler is Blocked?
The average lifespan of an EGR cooler is roughly 80,000 miles (128,7475 km), albeit it can be shortened by pre-existing flaws or damage from upstream problems. Over time, the carbon build-up can potentially clog the tubes and the EGR valve. If this occurs, your vehicle is likely to display a DTC code for inadequate EGR cooling. If the obstruction is straightforward, having your EGR cleaned rather than replaced might be more expedient and less expensive.
Additionally, the coolant lines in your EGR cooler may clog up with time. This is more typical in coolers using polluted or low-quality coolant or in older EGRs. You'll typically notice a decrease in EGR performance, a rise in fuel consumption, and problems with your engine overheating if your coolant lines are blocked. You can typically clean the lines if they are obstructed but undamaged instead of replacing them. Depending on your dealer and the amount of repair needed, this could take anywhere from 3 to 8 hours. On the other hand, leaking EGR coolers might also have the opposite issue.
How Do You Tell if the EGR Cooler is Leaking?
Exhaust gases that are as hot as 800°C are subjected to EGR coolers before being cooled to roughly 200°C. Old EGR coolers may crack or distort over time as a result of repeated exposure to extremely high temperatures, which can result in coolant leakage. The EGR cooler may corrode as a result of persistent wear or low-temperature particle condensation. The most typical indications of a leaky EGR cooler are as follows:
White Smoke: White exhaust smoke may indicate a coolant line leak where hot exhaust gas and coolant are combined. Low coolant levels can result from the hot exhaust burning the coolant.
Low Coolant Levels: This might also occur if the EGR cooler's outer shell develops a leak or break that allows coolant to escape.
Sticky/ Gooey EGR Valve: The carbon residue in the EGR valve may mix with coolant if it leaks into it. The valve becomes stuck as a result, making it difficult for it to open and close properly.
Check Engine Light: Any EGR issues will be detected if the check engine light comes on and you run a DTC scan. A fault code may indicate a clog or leak in the cooler, like "insufficient flow"!